What are EMI gaskets?
EMI gaskets are specialized components used to provide Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) shielding in electronic devices and systems.
Designed to block or reduce the transmission of unwanted electromagnetic signals that could interfere with the proper functioning of electronic components. EMI gaskets come in various forms, such as strips, sheets, O-rings, and custom shapes, and are typically made from conductive materials like metal or conductive elastomers.
By creating a conductive barrier EMI gaskets help:
- Prevent electromagnetic radiation from escaping or entering electronic enclosures, connectors, cables, and other critical areas.
- Ensure electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) and maintaining the reliable operation of electronic devices in environments with high electromagnetic noise.
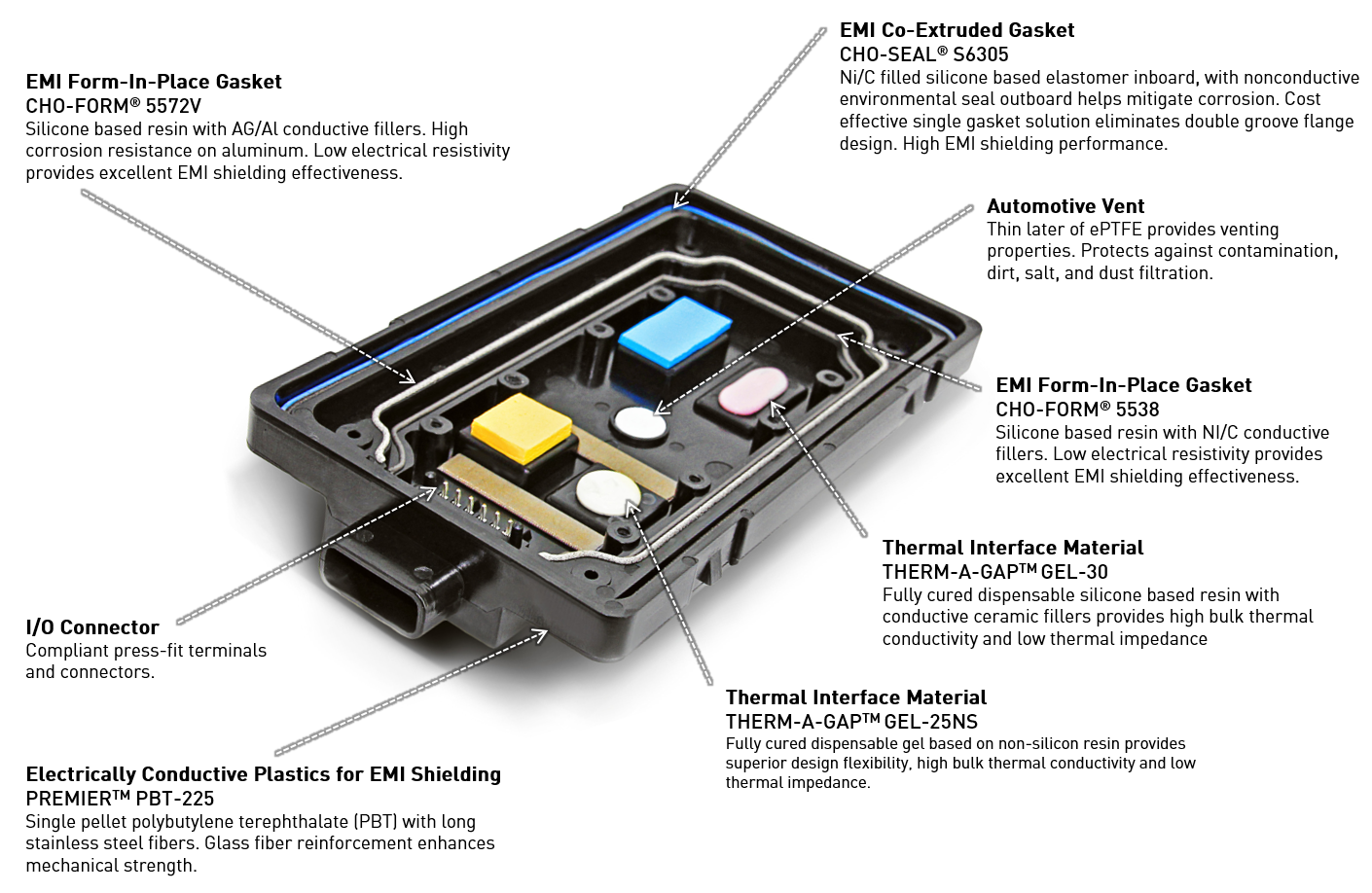
Integrated Gasket Solutions
Backed by Decades of Industry Experience
KraFAB can guide you toward the most cost-efficient, easily fabricable product on the market.
Experts ready to help you choose the best solution in eliminating gaps in the shielding coverage.
EMI Gasket Design
EMI gasket design involves selecting conductive materials and precise shapes to create a barrier against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) for electronic devices. Key considerations include material properties, size, compression, conductive contact, shielding effectiveness, environmental factors, and customization to address specific EMI challenges. By following these principles, engineers can develop effective EMI shielding solutions for reliable device operation in noisy electromagnetic environments.
Gasket Junction Design
Before choosing a gasket to work with, consider the variables for each
Each gasket is comprised of materials with individual benefits and are suitable for a specific application. KraFAB works with you to factor in a number of variables when selecting the right gasket, including:
- Compression forces
- Material compatibility
- Corrosion control
- Compression set
- Shielding performance
- Compression range
- Compressibility
- Environmental sealing
The best gasketing surface is not only rigid and recessed but also as conductive as possible. Metal surfaces touching the gasket should also be non-corrosive. When reaction with the environment cannot be avoided, the reaction products should be electrically conductive or easily susceptible to mechanical abrasion.
Many gasket designs fail, especially when mating to surfaces that are not treated correctly. The more imperfect the mating surfaces, the more critical the gasket function.
Perfect surfaces mean gaskets are not necessary. By perfect, we mean those with a solidly welded closure, infinitely stiff mating surface, or has complete conductivity across the junction. Engineers know perfect surfaces are expensive. Many may choose between economics and performance, but the design of the flange surfaces should not be compromised.
The important feature that makes a conductive elastomer gasket a good EMI seal is its ability to provide good electrical conductivity across the gasket-flange junction.
Generally, the higher the conformability and conductivity, the higher the shielding effectiveness. Surface conductivity of both the gasket and the mating surfaces is the single most important characteristic that makes the gasketed seam effective. Meaning, the resistance between the flange and gasket should be as low as possible.
Get in touch today with an expert today to discuss EMI shielding options to see if EMI gaskets will work for your next project!
Types of EMI/RFI Shielding Gaskets
EMI/RFI shielding gaskets come in various types, each designed to provide effective electromagnetic and radio frequency interference shielding. The main types of EMI/RFI shielding gaskets include:
- Conductive Elastomer Gaskets: Made from elastomeric materials filled with conductive particles (e.g., silver, nickel-coated graphite), conductive elastomer gaskets are flexible and provide excellent compression and conductive contact. They are commonly used to seal gaps and seams in electronic enclosures, connectors, and other applications requiring effective EMI/RFI shielding.
- Metal Gaskets: Metal gaskets are typically made from materials like stainless steel, aluminum, or copper. They offer high conductivity and mechanical strength, making them suitable for applications requiring robust EMI/RFI shielding performance.
- Fingerstock Gaskets: Fingerstock gaskets consist of a series of spring-like metal fingers that provide consistent pressure and conductive contact between mating surfaces. They are often used in shielded doors, connectors, and other applications requiring frequent access.
- Fabric-over-Foam Gaskets: These gaskets combine a conductive fabric or metal foil laminated to a soft foam core. Fabric-over-foam gaskets offer both flexibility and good shielding performance, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Wire Mesh Gaskets: Wire mesh gaskets are made from fine metal wires woven into a mesh structure. They provide good EMI/RFI shielding performance and are useful in applications where ventilation is required along with shielding.
- Conductive Foam Gaskets: Made from conductive foam materials, these gaskets offer good shielding performance and are suitable for applications requiring compressibility and resilience.
- Conductive Adhesive Tapes: While not traditional gaskets, conductive adhesive tapes are used to seal gaps and seams between components and enclosures. They provide a simple and effective solution for EMI/RFI shielding in tight spaces.
Each type of EMI/RFI shielding gasket is designed to meet specific shielding requirements and is chosen based on factors such as the level of shielding needed, the application, environmental conditions, and material compatibility with the mating surfaces.
Continue reading 6 Proven EMI Gaskets To Effectively Shield Interference, to see determine the best design for your project.
Understanding Conducted EMI and Its Impact on Electronic Systems
Conducted Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) refers to unwanted electromagnetic energy that is conducted along power or signal lines, rather than radiated through the air. This type of EMI can be categorized into two main components: differential-mode energy and common-mode energy.
- Differential-Mode EMI happens when unwanted electromagnetic signals appear between the conductors of a transmission line or power supply. It affects the information-carrying part of the signal, leading to data errors or distortion. It can be controlled by proper cable design, impedance matching, and filtering.
- Common-Mode EMI occurs when unwanted electromagnetic signals appear simultaneously on both conductors of a transmission line or power supply. It is induced by external electromagnetic fields or imbalances in the system. Common-mode interference can cause ground noise, disrupt communication, and is harder to suppress, requiring specialized filtering and grounding techniques.
Both differential-mode and common-mode EMI can negatively impact the performance and reliability of electronic devices and systems. To address conducted EMI, designers use various techniques, including the use of EMI filters, proper grounding, shielded cables, and careful layout and routing of traces. Additionally, adhering to electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) standards and best practices during the design and testing phases helps ensure that conducted EMI is kept within acceptable limits.
2 Types of EMI (Continuous vs pulse)
Continuous EMI
Continuous EMI, also known as continuous-wave EMI, refers to interference that occurs as a continuous and steady electromagnetic signal. It is characterized by a continuous waveform with no distinct breaks or interruptions. Continuous EMI sources can be devices or circuits that emit a constant electromagnetic signal, such as radio transmitters, microwave ovens, or power lines. Continuous EMI can affect electronic devices and systems by causing data errors, signal distortions, or disruptions in communication.
Pulse EMI
Pulse EMI, also known as transient EMI or impulsive EMI, refers to interference that occurs as short bursts or pulses of electromagnetic energy. Unlike continuous EMI, pulse EMI is characterized by its intermittent nature, with rapid changes in amplitude and duration. Pulse EMI sources can include devices with fast-switching components, electric motors, and lightning strikes. Pulse EMI can be particularly challenging to control due to its short duration and high peak energy. It can lead to abrupt voltage spikes, affect sensitive electronic components, and cause malfunctions or damage to electronic devices.
Similar to Conducted and Radiated EMI, the EMI shielding gaskets provide electromagnetic shielding by blocking unwanted electromagnetic signals, contain emissions, reduce crosstalk, and help devices comply with regulations.