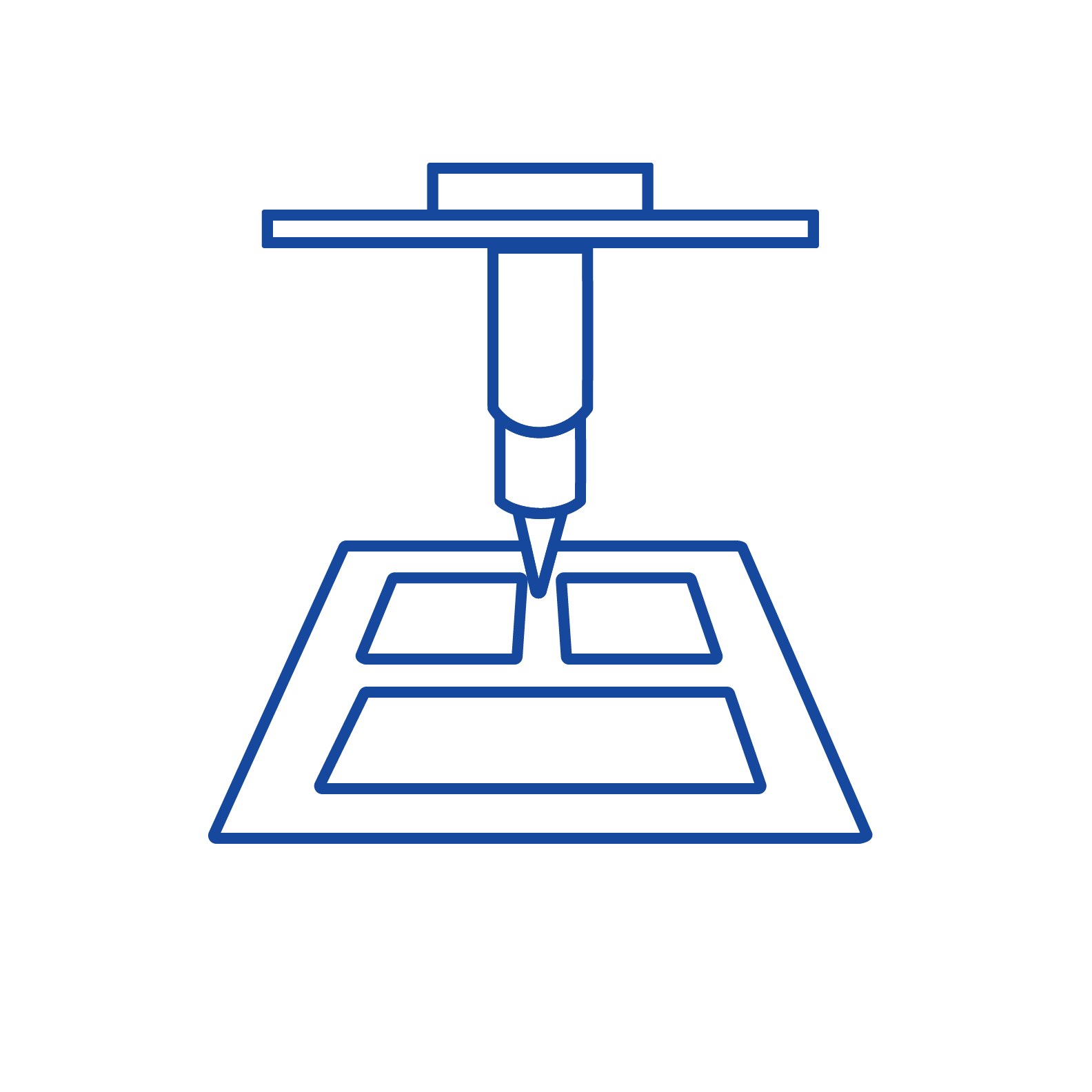
What is EMI Shielding?
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding is when conductive or magnetic materials act as barriers to block unwanted electromagnetic signals from entering the field. It impedes stronger signals from affecting its electronic surroundings and protects the more sensitive ones from escaping.
Understanding Electromagnetic Interference (EMI)
EMI itself is a disturbance that affects the operation of an electrical circuit, transmission channel or system. It can decrease or completely interrupt the performance of a circuit, and in extreme cases, even cause damage to the equipment.
This is caused by either:
Conduction – generated by physical contact between the affected circuits and source
Radiation – caused by induction, which is the motion of a conductor across a magnetic field or by a change in magnetic flux in a magnetic field.
Importance of EMI Shielding
In today’s interconnected world, where electronic devices and systems play a central role in nearly every aspect of our lives, the importance of EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) shielding cannot be overstated. EMI shielding is a critical component of the design and functionality of electronic equipment.
-
Protection of Sensitive Electronics
-
Maintaining Signal Integrity
-
Compliance with Regulations
-
Preventing Cross-Talk
-
Environmental Protection
-
Enhancing Security
-
Reducing Interference to Others
Backed by Decades of Industry Experience
KraFAB can guide you toward the most cost-efficient, easily fabricable product on the market.
Experts ready to help you choose the best solution in eliminating gaps in the shielding coverage.
Causes of EMI
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) refers to the disruption or degradation of the performance of electronic devices or systems caused by electromagnetic waves or signals. EMI can be categorized into two main types based on how it is induced: conduction-induced EMI and radiation-induced EMI. Here’s an explanation of the causes of each type:
Both conduction-induced and radiation-induced EMI can be detrimental to the proper operation of electronic systems, potentially causing data corruption, signal degradation, or equipment malfunction. To mitigate EMI, various techniques like shielding, filtering, grounding, and proper layout and design practices are employed in electronic and electrical systems.
EMI Shielding Techniques
Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) shielding techniques are used to prevent or minimize the unwanted transmission or reception of electromagnetic radiation, which can interfere with the proper functioning of electronic devices and systems. Two common EMI shielding techniques are isolation through physical shielding and suppression and desensitization. Let’s explore each of these techniques:
It’s important to note that EMI shielding is often a combination of multiple techniques. Design engineers consider factors such as the nature of the EMI source, frequency range, and the specific requirements of the electronic system to determine the most effective shielding approach.
EMI Shielding Attributes
Key EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) shielding attributes are crucial factors to consider when designing and implementing EMI shielding solutions for electronic devices and systems. These attributes ensure that the shielding is effective, reliable, and compliant with industry standards.

Excellent Shielding Effectiveness
K.R. Anderson FIP gaskets deliver extraordinary shielding effectiveness, surpassing 100 dB between 200 MHz and 12 GHz. This remarkable performance ensures robust EMI protection for sensitive electronic systems.
Programmable in 3 Axes
Full 3-axis motion of the application technology accommodates uneven surfaces that are common in castings or injection-molded parts. The result is enhanced control of the gasket cross-section.
Denser Packaging
FIP gaskets can be applied to walls or flanges as narrow as 0.030” (0.76 mm), and don’t require mechanical retention. Compared with groove and friction-fit designs, the positional accuracy and self-adhesive properties of our gaskets will typically save 60% or more space.
Small Cross Sections, Complex Geometries
Virtually any gasket bead path can be programmed using our application technology. In addition to simple straight lengths, the system applies continuous 360⁰ perimeter gaskets in combination with any required number of internal subpaths that form “T” joints with the perimeter seal.

Secure Gasket Adhesion
FIP gaskets provide secure adhesion to a range of common housing materials, including cast metal alloys with various coatings, nickel-copper plated plastics, stainless steel (300 series), and vacuum metalized aluminum. This ensures strong and lasting attachment for effective EMI shielding and environmental sealing.
Low Closure Force Not a Problem
FIP gasket materials are ideal for low deflection force designs, or those whose mating surfaces have low mechanical rigidity. Nominal deflection of 30% using a mechanical compression stop is recommended. Deflection below 20% or above 40% is not recommended.

Tight Control
FIP gasket beads are dispensed with an accuracy of 0.001 inch (0.025 mm). and a cross-sectional height tolerance of 0.006 inch (0.15 mm). This innovative technology produces clean bead ends minimizing the “tail” characteristic of other processes.
Quality Control
K.R. Anderson has the capability to perform automated dimensional verification of gasket bead placement and height for statistical process control, using fully programmable optical coordinate measuring technology and vision systems. Electrical resistance of cured gasket material is tested with a multimeter capable of measuring to 0.001 ohm.
EMI Shielding Using Gaskets
EMI shielding gaskets are specialized components used in electronic and electrical systems to provide a reliable seal while also offering electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection. These gaskets are designed to prevent the ingress or egress of electromagnetic radiation and electromagnetic interference, helping to maintain the integrity and performance of sensitive electronic equipment.
EMI shielding gaskets are specialized components used in electronic and electrical systems to provide a reliable seal while also offering electromagnetic interference (EMI) protection. These gaskets are designed to prevent the ingress or egress of electromagnetic radiation and electromagnetic interference, helping to maintain the integrity and performance of sensitive electronic equipment.
Challenges and Solutions in EMI Gasket Design
Designing effective EMI shielding gaskets comes with several challenges, including:
- Conductive Path Interruptions: Gaskets must provide a continuous conductive path to effectively block EMI. Gaps, seams, or irregularities in the gasket’s contact surface can lead to ineffective shielding. Solutions involve careful design and precision manufacturing to ensure a consistent and reliable conductive path.
- Compression Force: Achieving and maintaining the right compression force is crucial. Under-compression can lead to gaps in the shielding, while over-compression may cause mechanical damage or reduce the gasket’s lifespan. Proper material selection and gasket geometry help address this challenge.
- Environmental Resistance: EMI gaskets often need to provide environmental sealing in addition to EMI shielding. Designers must choose materials that can withstand various environmental conditions, including temperature extremes, moisture, and chemicals.
- Material Selection: The choice of elastomer material, fillers, and conductive particles can significantly impact the gasket’s performance. Careful selection is necessary to balance EMI shielding effectiveness, environmental resistance, and durability.
- Customization: EMI gaskets often need to be custom-designed to fit specific enclosure shapes and sizes. Customization ensures a precise fit and maximum shielding effectiveness.
Benefits of Metallic-Particle-Filled Silicone Gaskets
Metallic-particle-filled silicone gaskets, such as those containing silver, nickel, or other conductive materials, offer several benefits in EMI shielding applications:
- High Conductivity: The inclusion of metallic particles in the silicone matrix enhances the gasket’s electrical conductivity, providing excellent EMI shielding performance.
- Flexibility: Silicone-based gaskets are inherently flexible, making them suitable for applications with irregular surfaces or complex geometries.
- Resilience: Metallic-particle-filled silicone gaskets exhibit good resilience and compression set characteristics, allowing them to maintain their shape and sealing properties over time.
- Wide Temperature Range: These gaskets can often withstand a broad temperature range, making them suitable for diverse environmental conditions.
- Longevity: When properly designed and installed, metallic-particle-filled silicone gaskets can offer long service life, contributing to the reliability of electronic systems.
- Customizability: They can be tailored to fit specific enclosure designs and requirements.
Metallic-particle-filled materials, such as silicone, are able to combine the sealing properties of silicone rubber with the electrical properties of metals, making them among the top choices for gaskets.
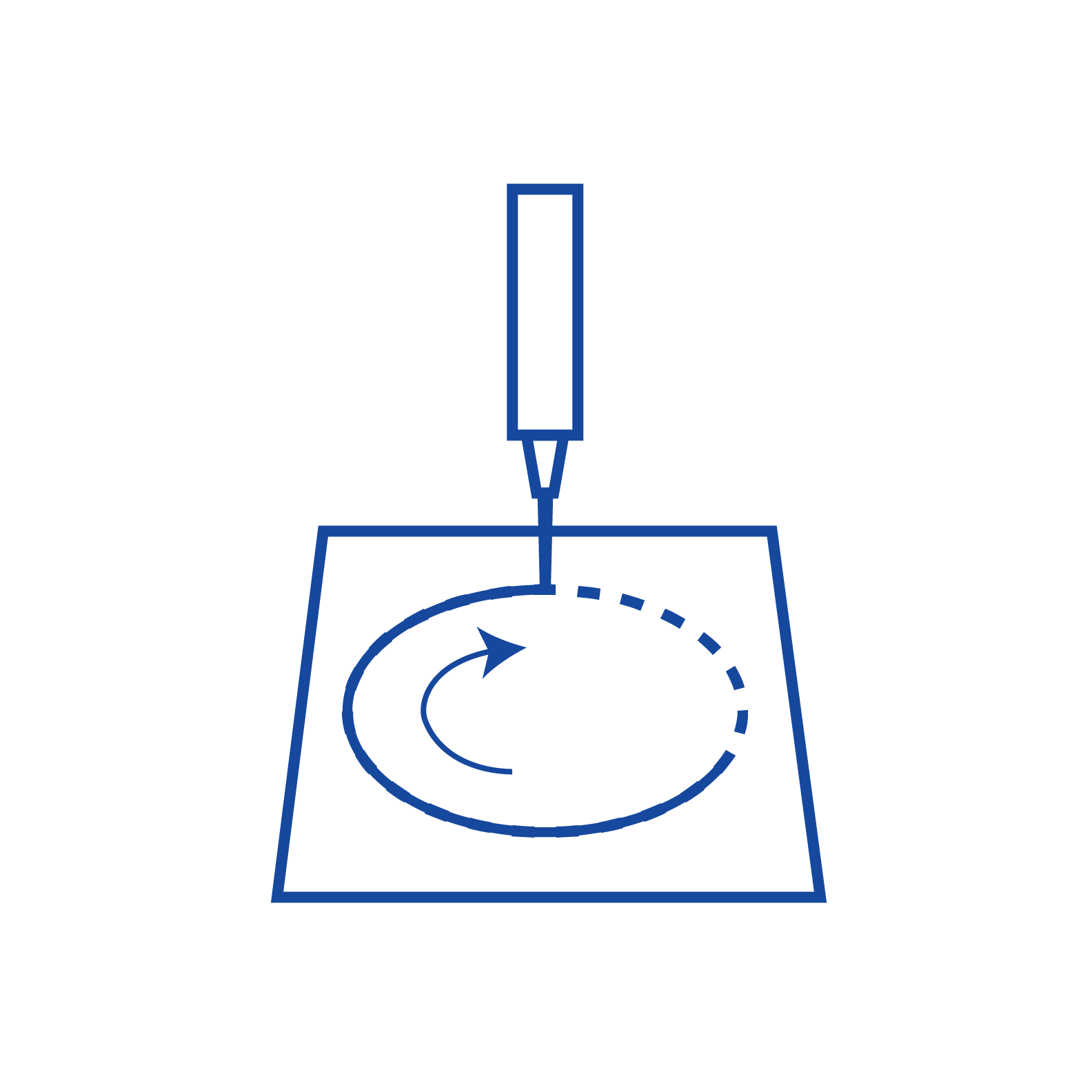
Form-in-Place EMI Gaskets
Form-in-Place EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) gaskets are a specialized technology used to provide effective EMI shielding and environmental sealing in electronic and electrical applications. Form-in-Place gaskets offer innovative solutions for enhanced EMI protection, cost savings, and thermal transfer benefits.
Form-in-Place (FIP) EMI gaskets are made from conductive elastomers, which are rubber-like materials filled with conductive particles, typically metal particles such as silver or nickel. What makes FIP gaskets unique is their application process. These gaskets are not pre-formed like traditional gaskets but are applied in liquid or paste form directly onto the surfaces that require sealing and EMI shielding.
Innovative Technology for Enhanced EMI Protection:
- Custom-Fit Solutions: FIP gaskets are highly adaptable and can be precisely applied to complex geometries, ensuring a custom-fit solution for sealing and EMI protection. This flexibility makes them suitable for a wide range of enclosures, connectors, and electronic components.
- Conductive Performance: The conductive particles in FIP gaskets create a conductive pathway, blocking or attenuating electromagnetic interference. This helps prevent EMI from entering or escaping the enclosure, protecting sensitive electronic components from interference.
- Environmental Sealing: FIP gaskets not only provide EMI shielding but also offer environmental sealing, protecting electronic equipment from dust, moisture, and other environmental factors.
- Highly Reliable: FIP gaskets are known for their durability and reliability. Once applied and cured, they maintain their sealing and shielding properties over time, even in challenging conditions.
Cost Savings and Thermal Transfer Benefits:
- Reduced Material Waste: FIP gaskets are applied directly to the required surfaces, reducing material waste compared to pre-cut gaskets. This can result in cost savings, especially for large-scale production.
- Elimination of Secondary Assembly: FIP gaskets eliminate the need for secondary assembly steps like cutting, handling, and placement of pre-formed gaskets. This streamlines the manufacturing process, reducing labor costs and potential errors.
- Thermal Conductivity: Some FIP gasket materials offer good thermal conductivity, which can help dissipate heat generated by electronic components. This is especially important for devices that require efficient thermal management.
Form-in-Place EMI gaskets are an innovative technology that offers custom-fit solutions for EMI protection and environmental sealing in electronic and electrical applications. They provide a cost-effective and efficient alternative to traditional pre-formed gaskets, reduce material waste, and can contribute to effective thermal management in electronic systems. These advantages make FIP gaskets a valuable choice for industries where EMI shielding, sealing, and cost efficiency are critical considerations.
Practical Applications of EMI Shielding using Form-In-Place Gaskets
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding has a wide range of practical applications across various industries. The primary purpose of EMI shielding is to prevent electromagnetic interference from affecting sensitive electronic components or systems.
EMI Shielding by Industry
Aerospace
Consumer Electronics
Industrial Electronics
Contact K. R. Anderson for EMI Shielding Design Support
Diverse EMI Shielding Solutions
EMI Shielding Design Support
Contact K. R. Anderson for design and manufacturing engineering support. We are one of the original Authorized Chomerics Distributor, Fabricator, and Form-In-Place gasket Application Centers in the United States.